Threes or Twos?
(The Study of Threes)
http://threesology.org
The following is another attempt to use Bigrams as so-called "Trigrams":
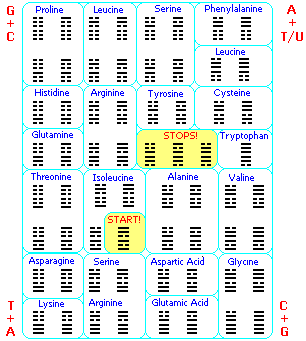
Amino acid positioning on the I Ching Matrix
|
Amino acid three letter codeFirst number is I ching number -- Second number is the binary value of the DNA codon and I Ching Hexagram.
http://www.cancun.com/sipp5/amino.stm
--- I Ching Genetic Code HyperDiamond Physics ---
http://www.innerx.net/personal/tsmith/ichgene6.html
In humanity's early attempts to unravel the genetic code, it was determined that in order for us to account for the 20 amino acids used in the synthesis of most proteins, there would have to be a code that would, at its very minimal, contain at least 20. As can be seen in the following chart, a singlet code would only provide us with 4 amino acid "words," and a doublet code would only provide us with 16 "words." It is obvious that both of these code formulas fall short of the minimum requirement of 20, but that a triplet code satisfies this need quite easily by having a 64 "word vocabulary":
| Singlet code (4 "words")
|
Doublet code (16 "words")
|
Triplet code (64 "words")
|
| AAA AAG AAC AAT | ||
| AGA AGG AGC AGT | ||
| ACA ACG ACC ACT | ||
| ATA ATG ATC ATT | ||
| GAA GAG GAC GAT | ||
| GGA GGG GGC GGT | ||
| A | AA AG AC AT | GCA GCG GCC GCT |
| G | GA GG GC GT | GTA GTG GTC GTT |
| C | CA CG CC CT | CAA CAG CAC CAT |
| T | TA TG TC TT | CGA CGG CGC CGT |
| CCA CCG CCC CCT | ||
| CTA CTG CTC CTT | ||
| TAA TAG TAC TAT | ||
| TGA TGG TGC TGT | ||
| TCA TCG TCC TCT | ||
| TTA TTG TTC TTT |
With the understanding that it takes three nucleotides to make up one "word" (called a codon), it is interesting to find that a sequence of codons (that we might refer to as a sentence), uses three "punctuation marks" called "stop codons," to end the sentence. There are 3 "stop" codons in RNA and 3 "stop" codons in DNA, along with 1 start codon for each, as is indicated in the following two tables. (We are thus presented with a 3 to 1 ratio formula that has cropped up in other areas:
Note that for each table, the left-hand column gives the first nucleotide of the codon, the 4 middle columns give the second nucleotide, and the last column gives the third nucleotide.
The RNA Codons:| U | C | A | G | ||
| U | UUU Phenylalanine (Phe) | UCU Serine (Ser) | UAU Tyrosine (Tyr) | UGU Cysteine (Cys) | U |
| UUC Phe | UCC Ser | UAC Tyr | UGC Cys | C | |
| UUA Leucine (Leu) | UCA Ser | UAA STOP | UGA STOP | A | |
| UUG Leu | UCG Ser | UAG STOP | UGG Tryptophan (Trp) | G | |
| C | CUU Leucine (Leu) | CCU Proline (Pro) | CAU Histidine (His) | CGU Arginine (Arg) | U |
| CUC Leu | CCU Pro | CAC His | CGC Arg | C | |
| CUA Leu | CCA Pro | CAA Glutamine (Gln) | CGA Arg | A | |
| CUG Leu | CCG Pro | CAG Gln | CGG Arg | G | |
| A | AUU Isoleucine (Ile) | ACU Threonine (Thr) | AAU Asparagine (Asn) | AGU Serine (Ser) | U |
| AUC Ile | ACC Thr | AAC Asn | AGC Ser | C | |
| AUA Ile | ACA Thr | AAA Lysine (Lys) | AGA Arginine (Arg) | A | |
| AUG Methionine (Met) or START |
ACG Thr | AAG Lys | AGG Arg | G | |
| G | GUU Valine Val | GCU Alanine (Ala) | GAU Aspartic acid (Asp) | GGU Glycine (Gly) | U |
| GUC (Val) | GCC Ala | GAC Asp | GGC Gly | C | |
| GUA Val | GCA Ala | GAA Glutamic acid (Glu) | GGA Gly | A | |
| GUG Val | GCG Ala | GAG Glu | GGG Gly | G |
The Genetic Code (DNA):
These are the codons as they are read on the (5' to 3') strand of DNA. Except that the nucleotide thymidine (T) is found in place of uridine (U), they read the same as RNA codons. However, mRNA is actually synthesized using the (3' to 5') as the template.
(This table is sometimes referred to as the Rosetta Stone of life.)| TTT | Phe | TCT | Ser | TAT | Tyr | TGT | Cys | |||
| TTC | Phe | TCC | Ser | TAC | Tyr | TGC | Cys | |||
| TTA | Leu | TCA | Ser | TAA | STOP | TGA | STOP | |||
| TTG | Leu | TCG | Ser | TAG | STOP | TGG | Trp | |||
| CTT | Leu | CCT | Pro | CAT | His | CGT | Arg | |||
| CTC | Leu | CCC | Pro | CAC | His | CGC | Arg | |||
| CTA | Leu | CCA | Pro | CAA | Gln | CGA | Arg | |||
| CTG | Leu | CCG | Pro | CAG | Gln | CGG | Arg | |||
| ATT | Ile | ACT | Thr | AAT | Asn | AGT | Ser | |||
| ATC | Ile | ACC | Thr | AAC | Asn | AGC | Ser | |||
| ATA | Ile | ACA | Thr | AAA | Lys | AGA | Arg | |||
| ATG | Met*** (START) | ACG | Thr | AAG | Lys | AGG | Arg | |||
| GTT | Val | GCT | Ala | GAT | Asp | GGT | Gly | |||
| GTC | Val | GCC | Ala | GAC | Asp | GGC | Gly | |||
| GTA | Val | GCA | Ala | GAA | Glu | GGA | Gly | |||
| GTG | Val | GCG | Ala | GAG | Glu | GGG | Gly | |||
| *** When within gene; at beginning of gene, ATG signals start of translation. | ||||||||||
The genetic code is almost universal. The same codons are assigned to the same amino acids and to the same START and STOP signals in the vast majority of genes in animals, plants, and microorganisms. However, some exceptions have been found. Most of these involve assigning one or two of the three STOP codons to an amino acid instead.
Mitochondrial genes:
When mitochondrial mRNA from animals or microorganisms (but not from plants) is placed in a test tube with the cytosolic protein-synthesizing machinery (amino acids, enzymes, tRNAs, ribosomes) it fails to be translated into a protein. The reason for this is that these mitochondria use UGA to encode tryptophan (Trp) rather than as a chain terminator. When translated by cytosolic machinery, synthesis stops where Trp should have been inserted.
In addition, most:
- Animal mitochondria use AUA for methionine not isoleucine and
- All vertebrate mitochondria use AGA and AGG as chain terminators.
- Yeast mitochondria assign all codons beginning with CU to threonine instead of leucine (which is still encoded by UUA and UUG as it is in cytosolic mRNA).
Plant mitochondria use the universal code, and this has permitted angiosperms to transfer mitochondrial genes to their nucleus with great ease.
The above table information and accompanying comments are adapted from:
http://www.ultranet.com/~jkimball/BiologyPages/C/Codons.html
Page Originated: Wednesday, 14th December 2011... 6:21 AM
Latest Update: Wednesday, 11th April 2018... 9:18 AM
Your Questions or Comments are welcomed:
Herb O. Buckland
(herbobuckland@hotmail.com}