(Trichotomic Thinking and Consciousness)
→→→ Tripartite Collection 1 ←←←
| EP 1 EP 1b |
EP 2 EP 2b |
EP 3 EP 3b |
EP 4 | EP 5 | EP 6 |
| EP 7 | EP 8 | EP 9 EP 9b |
EP 10 EP 10b |
EP 11 EP 11b |
EP 12 EP 12b |
Trichotomizologists as of Nov. 22, 2024
How dare you self-righteous religious leaders and leaders of Science, Philosophy, Mathematics, Psychology, as well as business and political leaders! How dare you turn away from the obvious to an extent that the word "Trichotomy" and its derivatives are not even a part of the terminology used by Psychology, and yet Psychologists the world over know all too well there is a persistent usage of dichotomies in teaching and the patient-care profession as disclosed by the adopted philosophy of dualities used in classroom instruction and the defining characteristic of many psychological states of affect such as ambivalence for schizophrenia, bipolarism (mania/depression), and many others where dichotomization is the primary idea of labeling behavior; but no effort is made in the use of an established Trichotomization in either the classroom or clinic. But don't take my word for it. Look for yourselves to see the absence of the word Trichotomization and its practice. And don't be surprised to encounter multiple intellectualized rationalizations as a defense mechanism when the departments of Psychology around the world are faced with a finger pointing out their practiced ignorance for which the public has suffered with for far too long. Instead of binding the public's feet, the clinics and classrooms of psychology have bound the body, mind, and soul of humanity. And the result? Look at the mental health crisis in business, government, and religion. Such is the case for this Age of Irrationality.
3rd planet from the Sun: Earth3 basic layers to Earth: Crust~ Mantle~ Core
***Earth's shape is sometimes referred to as a triaxial ellipsoid
333,000 times that of the Earth: The Sun's "approximate" Mass
3 degrees: Temperature of Outer Space (middle point between 2.5 to 3.5 range)
3 atmospheric gas content constants on Earth: 78% Nitrogen~ 21% Oxygen~ 1% all other gases
3 theories concerning form of Universe: Flat ~ Spherical ~ Saddle Shaped (Linear~ Circular~ Triangular)
3 phenomena of Big Bang theorists: Helium abundance~ Microwave background~ Hubble expansion
333 miles per hour: Earth's "approximate" rate of spin
3 variations to Earth's rotation:
Secular (Friction from Earth's tidal bulge) ~
Periodic (Seasonal changes & regular events) ~
Irregular (Turbulent core/mantle interactions)
3 (23.5°) measurements of Earth:
- The Earth's axis sweeps out a cone of 23.5° half angle in 26,000 years
- Summer solstice from equator
- Winter solstice from equator
3 families of fundamental particles based on a psychological dispostion:
- Those that are Stable (sane).
- Those that are Unstable (neurotic).
- Those that are highly Unstable (insane).
3 parts of an atom: Neutrons~ Protons~ Electrons
3 basic parts to fundamental parts of atoms: 3 Quarks and 3 Anti-Quarks
3-based fractionization of Quarks: Up (2/3rds)- Top 2/3rds)- Charmed 2/3rds); Down (1/3rd)- Bottom (1/3rd)- Strange (1/3rd)
3 content percentages of Gunpowder: 75% Potassium nitrate~ 15% Charcoal~ 10% Sulfur
3 basic components to nitroglycerine: Glycerol~ Nitric acid~ Sulfuric acid
3-lettered explosive (TNT) Tri-nitrotoluene, is a standard by which all other explosives are measured for 1) cost, 2) transport, and 3) flexibility of use.
3 processes of nuclear energy: Fission ~ Fusion ~ Combination(?)
3 Big Bangs:
- The "original" Big Bang of the Universe. (13.8 billion years ago.)
- Mammoth explosion of a nearby massive star.
- 65 million year old "Dinosaur killer" rock that caused a nuclear winter.
***Triple alpha process occurring in the interior of stars at 100 million degrees is responsible for the nuclear formation of carbon
3 classical origin of Moon hypothesis:
- Binary planet or "sister" hypothesis~
- Rotational fission or "daughter" hypothesis~
- Capture or "wife" hypothesis
3 major (Moon) rock types: Potassium-rich basalt, Anorthosite, An Iron, Titanium-rich basalt
3 Universe Cosmology of J.R. Gott III: Our Universe~ Antimatter Universe~ Tachyon Universe
 3 basic forms of Matter on Earth: Solids- Liquids- Gases (adding the external-to-Earth plasma makes the count a 3 to 1 ratio)
3 basic forms of Matter on Earth: Solids- Liquids- Gases (adding the external-to-Earth plasma makes the count a 3 to 1 ratio)3 basic Rock forms: Igneous~ Metamorphic~ Sedimentary
3 forms of Carbon: Diamonds~ Graphite~ Fullerene
3 forms of Atomic radiation: Alpha- Beta- Gamma
3 general laws of Thermodynamics (1st, 2nd, 3rd laws are distinguished from the Zeroth law)
3 laws of Planetary Motion (Johannes Kepler)
3 laws of motion (Isaac Newton)
3 basic Hydrodynamic laws
3 Robotic laws: Isaac Asimov
3 Magnetism "laws": Opposites attract~ Likes repel~ Inverse square
3 basic materials used in magnets: Iron~ Cobalt~ Nickel
3 millimeters thick is considered a typical magnet by some standards
3 magnetic materials: Hard~ Soft~ Semi-hard (recording materials)
***Triplets are the most commonly found phosphorescing states
3 major wavelengths of sunlight: Visible~ Ultraviolet~ Infrared
3 ultraviolet radiation divisions:
- Near (4,000- 3,000 Å) ~
- Middle (3,000- 2,000 Å) ~
- Long (2,000- 100 Å)
3 fundamental forces of nature: Gravitational~ Nuclear~ Electromagnetic
3 fundamental forces in agreement with the Standard Model: Weak- Strong- Electromagnetic; 1 force not in agreement: Gravity
3 "ideal gas" laws: Robert Boyle's~ J. Charles or J. Lussac's~ Avogadro's
(These 3 explain {in a 3 to 1 ratio way} how Pressure~ Temperature~ Volume + number of particles in a container of gas are related.)
RNA~ DNA~ Proteins RNA: --- Predominantly single stranded 3 main types: Messenger (mRNA)- Ribosomal (rRNA)- Transfer (tRNA) 3 triplets terminate protein synthesis: UAG- UAA- UGA; 1 triplet starts it: 3-site tRNA model is well established, 2-site model is dead DNA --- Predominantly double-stranded (Double Helix) 3 polymerases (enzymes): DNA Polymerase I- II- III 3-patterned (triplet) codon system Proteins: --- Predominant triple conformation structure 3 single polypeptide forms: Primary~ Secondary~ Tertiary 3 secondary structure regions: Alpha helix~ Beta sheet~ Looped 3 tertiary structure domains: Alpha helix~ Beta sheet~ Combination of both (1 multiple polypeptide structure called Quaternary, is a composite) |
3-to-1 ratio DNA/RNA structure: 3 amino acids the same (Adenosine- Cytosine- Guanine) and 1 is different; Thymine (DNA)/ Uracil (RNA)
3-stranded Collagen is considered most abundant protein in our body (Triple Helix)
3 component nucleotide: Nitrogenous base~ Pentose sugar~ Phosphate group
***Tribonucleic acid (TNA), consisting of a hemiactal backbone of surface-anchored phosophotrioses, has been proposed as a hypothetical precursor to RNA and DNA, by G. Wachtershauser, 1988.
3 Billion base pairs: common reference to the human genome
3 common references to quantity of cells in the human body: 1 trillion~ More than a trillion~ 100 trillion.
3 cell membrane theories: (1st) Monolayer~ (2nd) Bi-lipid layer~ (3rd) Trilaminar
3 (gases) to 1 (water) ratio for Chemical Evolution conducted by Stanley Miller: Methane~ Hydrogen~ Ammonia + water
3 distinct Cytoskeleton components: Microtubules~ Actin Filaments~ Intermediate Filament
 3 primary cellular energy molecules: AMP~ ADP~ ATP (ATP is primary energy source)
3 primary cellular energy molecules: AMP~ ADP~ ATP (ATP is primary energy source)3 groups of basic cells: Eubacteria~ Archaebacteria~ Eukaryotes
3 germinal layers: Endoderm~ Mesoderm~ Ectoderm
3 sequenced organism development: "Monoploblastic"~ Diploblastic~ Triploblastic
3 ionized forms of amino acids: Nonpolar~ Polar~ Electrically charged
3-lettered abbreviations used for amino acids
3 types of molecular bond: Covalent~ Ionic~ Polar covalent
3 isomerism types:
- Structural (Ethyl alcohol)~
- Geometric (Maleic acid)~
- Optical (L-Lactic acid
3 hydrocarbon chain types: Straight (Propane)~ Branched (Isobutane)~ Circular (Cyclopropane)
3 main fatty acid categories: Saturated~ Monounsaturated~ Polyunsaturated
*** Omega-3 family of Essential Fatty Acids is said to be needed for optimum health
3 basic chemical reaction substances: Acids~ Bases~ Salts
3 layers of Arteries, Capillaries, Veins: Connective tissue~ Muscle~ Endothelium
(Tunica intima~ Tunica media~ Tunica adventia)
3 dietary monosaccharides well absorbed: Glucose~ Galactose~ Fructose
3-patterned general formula for carbohydrates: Cx(H20)y
3 metabolized for energy needs: Carbohydrates~ Fats~ Proteins
Triglycerides are the main storage forms of fatty acids
3 flow pattern types of Pulmonary Circulation:
- Zone A (Alveolar pressure exceeds intravascular pressure)~
- Zone B (Alveolar pressure intermediate between arteriolar and venular pressures)~
- Zone C (Intravascular pressure exceeds alveolar pressure)
3 classes of Amines (ammonia compounds):
- Primary, NH2R ~
- Secondary, NHR2 ~
- Tertiary, NR3
3 classes of Neurons: Motor (Monopolar)~ Sensory (Bipolar)~ lnter (Multipolar)
3 main cellular components of Blood: Red blood cells~ White blood cells~ Platelets
3 blood plasma protein groups: Globulin~ Albumin~ Fibrinogen
3 white blood cell (leucocyte) groups: Granulocyte~ Lymphocyte~ Monocyte
3rd corpuscle: (alternate name for platelets)
*** Band 3 protein is complex molecule in red blood cell (erythrocyte) membranes
3 letters (and combinations thereof) used for blood typing: (A~ B~ 0)
3 main blood channels: Veins~ Arteries~ Capillaries
3 interferon types: (White blood cells)~ (Fibroblasts-connective tissue)~ (Lymphocytes)
3 gastrointestinal tract wall layers: Epithelium~ Lamina propria~ Muscularis mucosae
3 gastric mucosa regions: Cardiac glandular~ Oxynti glandular~ Pyloric glandular
3 parts of the small intestine: Duodenum~ Jejunum~ Ileum
3 types of (digestive tract) epithelial cell junctions: Tight~ Desmosome~ Gap
3 carbon-to-carbon bonds:
- Single (Ethene)
- Double(Ethylene)
- Triple (Acetylene)
3 genotypes: AA (homozygous dominant)~ aa (homozygous recessive)~ Aa (heterozygous)
*** Since the fertile life of the human egg cell lasts at most one day and that of the human sperm at most two days, there is a period of about three days during which copulation can result in conception (the day when the egg is fertile and the two preceding days).
*** Generally speaking, the egg traverses the fallopian tube in about 3 days; Sperm can travel at a rate of 3 inches per hour; A spermagonium gives rise to 3 active cells and 1 resting cell.
3 trimester divisions in pregnancy
3 bones of the pelvic girdle: Ilium~ Pubis~ Ischium
3 stages of labor: Dilation of the cervix~ Delivery of the baby~ Delivery of the placenta
3 days after birth is a baby's customary first check-up
3 months old is when most babies begin shedding tears.
3 stages to ovarian follicle development
3 layers to female uterus: Perimetrium ~ Myometrium ~ Endometrium
3 embryonic somites: Dermatomes ~ Myotomes ~ Sclerotomes
3 membranes surround embryo: Amnion~ Chorion~ Allantois
3 expansions of neural tube produce: Forebrain ~ Midbrain ~ Hindbrain
3 successive brain divisions: Hind/Midbrain ~ Limbic system ~ Cerebral cortex
3 brain and spinal cord layers: Pia Mater~ Dura Mater~ Arachnoid process
3 Spinal Cord white-matter columns:
- Dorsal Funiculus ~
- Lateral Funiculus ~
- Ventral Funiculus
3 pounds: common reference to the weight of the human brain
3 pints: common reference to the capacity of the human brain
3 stages of brain development: Reptilian ~ Mammalian ~ Neomammalian
3 lobes on each Cerebellum hemisphere: Blocculondodular ~ Anterior ~ Posterior
3 divisions of autonomic neurons: Sympathetic ~ Parasympathetic ~ Enteric
3 major classes of endogenous opioid peptides: Enkephalins~ Endorphins~ Dynorphin
3 basic epithelial cell shapes: Squamous ~ Cuboidal ~ Columnar
3 heart layers: Endocardium ~ Myocardium ~ Pericardium
3 forms of stroke: Embolic ~ Hemorrhagic ~ Thrombotic
3 Catabolism stages: Glycolysis ~ Conversion of Pyruvic acid into acetyl CoA ~ Krebs Cycle
3 important nitrogenous waste compounds: Ammonia~ Urea~ Uric acid
3 bands of the Colon: Teniae mesocolica~ Teniae libera~ Teniae omentalis
3 histochemical types of skeletal muscle fibers: Type I~ Type IIB~ Type IIA
 3 types of taste bud groups on papillae: Circumvallate~ Foliate~ Fungiform
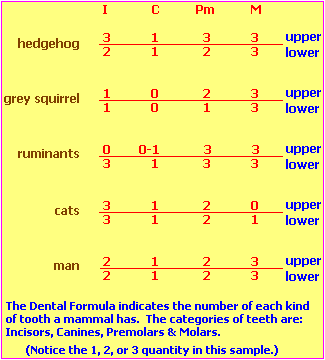
3 types of taste bud groups on papillae: Circumvallate~ Foliate~ Fungiform3 molars, 2 bi-cuspids,1 cuspid on both sides and both lower/upper jaws
3 tooth parts: Crown~ Neck~ Root
3 bud parts: Enamel organ~ Dental papilla~ Dental Sac
3 surface divisions of tooth: Lingual - Facial - Proximal
***Triangular shape to canine tooth roots in cross section
3 main types of malocclusions: Overbite ~ Underbite ~ Crowding
3 (1st, 2nd, 3rd) lower & upper jaw molars
3rd molar is singled out to be called the wisdom tooth.
3 main stages to periodontal (Gum) disease: Gingivitis ~ Periodontitis ~ Loss of bone
3 main kinds of periodontal diseases: Gingivitis ~ Periodontitis ~ Vincent's Infection
3 most common artificial teeth types: Bridges ~ Partial dentures ~ Full dentures
3 muscle types: Striated ~ Cardiac ~ Smooth
3 muscle divisions: Head ~ Belly ~ Tail
3 gluteus muscles: Maximus ~ Medius ~ Minimus
3 muscle fiber arrangements: Unipennate ~ Bipennate ~ Multipennate
3 masseter muscle parts: Superficial ~ Intermediate ~ Deep
3 muscle heads: Biceps ~ Triceps ~ Quadriceps ("Quadricep" refers to Musculus Triceps Surae, the Plantaris is counted separately) {another 3:1 ratio}
3 muscle (contrasts) definitions: Superior/Inferior~ Major/Minor~ Posterior/Anterior
3 lateral vertebral muscles: Scalenus anterior~ Scalenus medius~ Scalenus posterior
3 peroneal/fibular muscles: Peroneus brevis~ Peroneus longus~ Peroneus tertius
3 general muscle attachment types: Superficial fascia ~ Deep fascia ~ Subserous facia
3 eyelid muscles: Levator palpebrae superioris ~ Obicularis oculi ~ Corrugator supercili
3 parts of the eye: Iris~ Cornea~ Pupil
3 orbicular muscle portions: Pars orbitlis ~ Pars palpebralis ~ Pars lacrimalis
3 color blindness types: Protanopia ~ Deuteranopia ~ Tritanopia
3 eyeball tissue layers: Sclera/Cornea ~ Uveal Tract ~ Retina
3 preotic myotomes of the eyes: Oculomotor ~ Trochlear ~ Abducens
3 eyeglass types: Monofocals ~ Bifocals ~ Trifocals
3 extrinsic straight muscles (eyes): Lateralis rectus - Medialis rectus - Superior rectus
3 parts of the eye: Iris - Cornea - Pupil
3 color blindness types: Protanopia - Deuteranopia - Tritanopia
3 eyeball tissue layers: Sclera/Cornea - Uveal Tract - Retina
3 "convenient" pelvic fascia divisions: Piriformis ~ Obturator ~ Superior
3 columns (with 3 subdivisions) of the erector spinne (sacrospinalis) muscle mass:
(Lateral column): Ilicostalis lumborum~ Iliocostalis thoracis~ Ilicostalis cervicis;
(Intermediate column): Longissimus thoracis~ Longissimus cervicics~ Longissimus capitis;
(Medial column): Spinalis thoracis~ Spinalis cervicis~ Spinalis caphis
3 divisions to the transversospinalis muscle group:
- Semispinalis thoracis~ Semispinalis Cervicis~ Semispinalis capitis
- Multifidus muscles
- Rotatores thoracis~ Rotatores cervicis~ Rotatores lumborum
*** The human knee performs one kind of movement (flexion/extension)~ The ankle performs two kinds of movement (flexion/extension & inversion/eversion)~ The ball-and-socket joints, such as the hip, allow three degrees of freedom.
3 between-finger triangular spaces for each hand
3 stomach wall fiber layers: Longitudinal~ Circular~ Oblique
3 layers of dead cells make up a hair shaft: Medulla~ Cortex~ Cuticle
Triphasic sexual response nature:
- Female): Desire~ Lubrication & Swelling~ Orgasm
- (Male): Desire~ Erection~ Ejaculation
3 stages of sexual behavior by sex "experts": Foreplay~ Loveplay~ Afterplay
3 immature "standards" of sexual behavior: Length of penis~ Frequency of sex~ Number of orgasms
3-part phrase of insecure, barbaric, egocentric men: Wam - Bam - Thank you ma'am
3-part motto attributed to British Special Air Services (SAS) Regiment:
Get in- Get it done- Get out
3 functions of human skeleton: Support~ Protects organs~ Movement (with muscles)
3 letters (and combinations thereof) used for blood typing: A - B - 0
3 main blood channels: Veins - Arteries - Capillaries
3 days after birth is a baby's customary first check-up
3 months old is when most babies begin shedding tears
3 amino acids associated with organisms having a thyroid gland: Monoiodotyrosine - Diiodotyrosine - Triiodothyronine
3 stages of brain development: Reptilian - Mammalian - Neomammalian
3 skin layers: Epidermis - Dermis - Subcutaneous Tissue
3 burn degrees: 1st degree burn - 2nd degree burn - 3rd degree burn
3 trimester divisions in pregnancy
3 layers to female uterus: Perimetrium - Myometrium - Endometrium
3 basic fingerprint types: Loop - Whorl - Arch
3 basic feather types: Contour - Down - Filoplumes
3 parts of the small intestine: Duodenum - Jejunum - Ileum
3 bones of the pelvic girdle: Ilium - Pubis - Ischium
3 animal reproduction types: Oviparous - Viviparous - Ovoviviparous
3 animal feeding types: Herbivore - Carnivore - Omnivore
3 main body parts to Arthropods: Head - Thorax - Abdomen
3 segments of insect thorax: Prothorax - Mesothorox - Metathorax
3 eyelids in the Tuatara, Crocodilians and most birds
3 groups of Ocean life: Plankton - Nekton - Benthos
3 muscles of the human nose: Procerus - Nasalis - Depressor septi
3 elevations (Concha) in the olfactory portion of the nose
3 bones in the nose: Inferior Meatus - Middle Meatus - Superior Turbinate
3 stages of bone development: Membranes - Cartilaginous - Osseous
3 types of cartilage: Fibro - Elastic - Hyaline
3 possible bone formation sites: Intramembranous - Endochondral - Heterotopic
3 bone layers: Concentric - Circumferential - Interstial
3 bone cell types: Osteoblasts - Osteocytes - Osteoclasts
3 joint categories: Fibrous - Cartiloginous - Synovial (Immovable - Partly movable - Freely movable)
3 stage development for some insects: Larva - Pupa - Imago
3rd and usually largest vein of an insect's wing is called the Radius
3 plant families of trees with the most significant (food bearing) attractive flowers: Magnoliaceae - Rosoceae - Leguminosae
3 "feeding" hairs on Venus fly trap lobes trigger closing
3 flagella on certain protozoans (Tritrichomonas)
3 sets of chromosomes in humans (presently) produces mutations such as Down's syndrome
3 sets of chromosomes in plants produces humanity's single most important food sources such as maize, wheat, barley, oats, rice and other cereals (Monocotyledonea plants)
3 photoperiodic plant types: Long day - Day-neutral - Short day
3... Robert Sternberg's (Psychology) Triads:
Roger Penrose, in his book Shadows of the Mind, outlines an idea adapted from Karl Popper – that there are "three worlds." The physical universe needs no explanation, except perhaps to Bishop Berkeley, while the subjective world of our own conscious perceptions is one we each know well. The third world is the Platonic world of mathematical objects.
Page Initiated: Saturday, 14th December, 2024... 8:01 AMInitial Posting: Tuesday, 17th December, 2024... 2:14 PM