Page C
(The Study of Threes)
http://threesology.org
This page is a companion to the following links:
- Evolutionary 3s page A
- Evolutionary 3s page B
- Evolutionary 3s page D
- Evolutionary 3s page E
- Evolutionary 3s page F
3 likely possibilities of how an (accidental) fire may have occurred when discovered as remains at an excavation site, if such did not occur by the hand of early humans:
- Volcanic action
- Spontaneous vegetable combustion
- Lightning or,... (Meteors~ Sun~ Lightning)
***de Mortillet said: "The mammalian fauna has been replaced several times, at least thrice, since the implement-bearing deposits at Thenay were laid down.
***de Mortillet called the precursor to modern humans the genus Anthropopithecus, which he thought existed in three species: The oldest, that of Thenay, being the link with the apes. The other two species were the makers of flint tools found by Ribeiro in Portugal and by Rames at Aurillac in Southern France.
3 (abbreviated) distinct stages of early peoples utilizing bog ore from swamps to smelt iron, according to Arlington H. Mallery in his book "Lost America":
- Ore was piled up in heaps on layers of wood fagots and heated or calcined until it was red.
- Mixed with fuel and burned in a smelting furnace operated at a temperature below the melting point (about 2100 degrees) of cast iron.
- Quenched with fire and then beaten to remove slag.
3 part composition of bog ore: Clay~ Loam~ Hydrated oxides of iron.
3 periods of the Wisconsin (final North American glacial age): Early~ Middle~ Late (or main).
***Since the half-lives of Uranium~ Thorium ~ Protactinium are known, it is thought that by measuring the amounts of these elements present within a sample, the age can be calculated.
3 items, Mortar ~ Pestle ~ Seeds/grains/etc., can be said to be unconsciously derived symbolic representations of the:
- Vagina = (mortar)
- Penis = (pestle)
- "Mixing seeds, etc.," into a concoction
...which is a symbolic representation of mating and producing a child?
The date ranges for 3 species of hominid are said to overlap:
- Lantian man, a primitive Homo erectus
- Peking man, a more advanced Homo erectus
- Tongzi man, described as Homo sapiens
3 era divisions with three subdivisions:
(Pleistocene) Early ~ Middle ~ Late {each of which contains its own early ~ middle ~
late subdivisions}.
| 3 categories of explanation for modern human
origins: The 3 categories of human origin explanations are frequently referred to as two major hypothesis labeled Replacement & Regional Continuity Theories, with the third category in the above list sometimes "lumped" into one or both of these two as being some sort of appendage without legs to support itself. However, if you don't agree:
In short, the 3rd view is somewhat of a combination of the two previous views... or, a type of 3 into 1 ratio theory. |
Yes, the three phrases:
- "evolutionarily - inferior"
- "separate but evolutionarily - equal"
- "individualized but evolutionarily - comparative"
... are intentional politically - oriented references in an attempt to broaden your appreciation of underlying comparisons that may be made by those who think there are ulterior social conspiracies associated with these anthropological ideas.
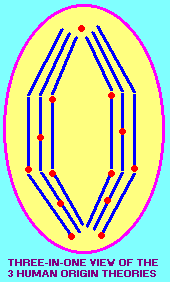
By using a rather museful approach towards stretching the imagination to describe these three views, the following images suggest that the "3 HOT's" (three Human Origin Theories) represent a macroscopic representation of an event which takes place on a microscopic cellular level. An extension of this idea would be to include the three traditional racial classifications as an additional example of "migrating bodies":
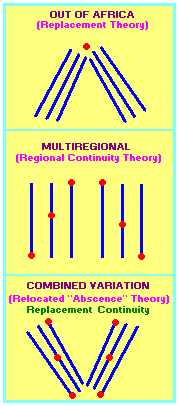 |
 | |
You might want to think that the little red "dots" are temporary human migration "settlements." |
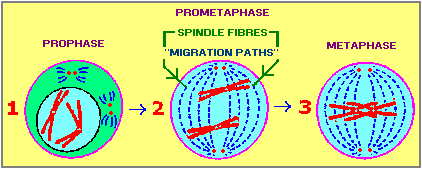
 Compare this with the above metaphase image. |
|
 |
||
3 traditional classifications of "migrating" races:
- Negroid
- Mongoloid
Caucasoid
- Homo sapiens>/LI>
- Homo troglodytes (cave man)
- Homo ferus (wild man)
- Observed wildmen in natural surroundings.
- Observed dead specimens.
- Observed live captured specimens.
- Five of them thought the skull to be an anthropoid ape
- Seven thought it human
- Seven considered it intermediate
- Chemical Evidence
- Radiometric
- Stratigraphic
- We should have found their bones in North America by now.
- Why haven't hunters shot one in North America yet?
- Why aren't there more photos of these modern gigantos?
- 3 toes have been indicated in some footprints of Big Foot.
- The giant sized, five-toed prints resembling a Homo sapiens foot pattern.
- Some in Asia demonstrate a five toed pattern wherein:
- The big toe is enormously broad
- The middle toe is excessively long and...
- The other three are tiny on a foot resembling a baseball catcher's mitt.
Evolutionary systematics: The traditional approach based on homology and the scientist's best judgment of the closeness of relationships. Homology is similarity by descent. Homology is determined by ancestor/descendant relationships.
Phenetics: Grouping of species bases on phenotypic similarity (Much molecular systematics follows this path).
Cladistics: Arrangement of taxa based on two main ideas:
- Begin by acting as if all traits are homologous.
- Use only "shared-derived" characters to group lineages.
- Synapomorphy- shared derived character states.
- Sympleisiomorphy- shared primitive states.
- Homoplasic- shared but independently evolved state.
- (3 versus 1 and 2 is a question of homology.)
- (1 versus 2 is a question of polarity-- direction of evolution)
- Any group of organisms are related by descent from a common ancestor.
- There is a bifurcating pattern of cladogenesis.
- Change in characteristics occurs in lineages over time.
Divergent Evolution - Divergent evolution occurs when a single group of organisms splits into two groups and each group evolves in increasingly different directions.
Parallel Evolution - Parallel evolution occurs when a group of organisms evolve into two distinct but similar lineages and continue to adapt in similar ways for a long period of time, often in response to a similar environment.
Convergent Evolution - Convergent evolution is evolutionary change in two or more unrelated organisms that results in the independent development of similar adaptations to similar environmental conditions.
- Discover all species.
- Reconstruct phylogeny (genealogical relationships).
- Classify according to phylogeny.
(Some modern researchers include another group, Australoid, which gives us a another 3 to l example.) See the information via the following link for other 3 to 1 examples:
http://www.threesology.org/321-a.php
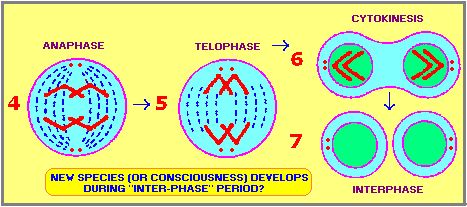
(For those with a penchant of interpreting every numerical reference to some biblical context, the above "Interphase" associated with the number 7 should bring to mind that on the seventh day, God rested... and this is when Adam and Eve snuck into the apple orchard, or was it a fig grove, or pomegranate bush? With respect to the idea of a biblical reference to an apple (and hence, an apple orchard), one must wonder whether the apple was of a pre-modern size, rendering it as a form of (small) crab-apple. Maybe it was a lemon or some other item misidentified. Anyway, the rest is history.
A more contemporary view of humanity distinguishes a 3 X 3 (9 groups of people) distribution of racial classification amongst the various geographical areas of Earth:
African, European, Asiatic, American Indian, Indian (India), Australian, Polynesian, Micronesian, Melanesian...+ an additional group comprising those peoples that are said to not be easily classified in any of these taxonomies, which results in a 3 X 3 to 1 ratio.
Not every genetically determined set of traits has equal value in (1) Comparing~ (2) Differentiating~ (3) Searching for the origin of each race.
3 areas where major African Homo sapiens fossils are found: North Africa~ East Africa~ South Africa.
In 1923, O. Zdansky discovered a single human tooth at Choukontien, locality 1. In 1926, amidst a mass of animal fossils taken from there to Upsala in Sweden to be studied, another human tooth was found. In 1927, Birgiv Bohlin discovered another tooth. After these (three) were found, Dr. Davidson Black, after concentrated study, announced the discovery of a new human genus and species, "Sinanthropus pekinensis" (Chinese man of Pekin). The last (3rd) tooth was taken on a world tour by Dr. Black.
It is interesting to consider whether the activity of modern peoples to set up camp near the remains of ancient camp sites is similar to those individuals of the supposed ancient camp site as a group who also had camped near the camp grounds of an earlier group which camped nearby.
3 super-imposed faunas were identified with a skull found in 1960 from a cave in Thessaloniki in Eastern Greece. The (Petralona man) skull has been linked to the oldest of the three faunas which suggests the skull is older than the later middle Pleistocene.
3 pieces of a skull were found in the Thames Middle Gravels at Swanscombe in North Kent, England. Two parts of the (Swanscombe man) skull were found in 1935 & 1936, and the third part about 20 years later.
In 1775, Carl Linnaeus, the founder of the modern system of biological classification, listed three existing human species:
Since 1775, scientists have:
And if we include the collection of physical evidence for wildmen, including hundreds of footprints, we have another 3 to 1 example.)
Pongids are the anthropoid apes such as Chimpanzees, Gorillas, Orangutans.
3 main danger calls of the vervet monkey: for Snakes ~ Feline predators - Avian predators (low ~ medium ~ high predation)
In 1896, Eugene Dubois assembled the opinions of nineteen other authorities on his "Pithecanthropus erectus" discovery:
Did ancient peoples "hang out" in groups of 1~ 2~ 3 people?
Three methods frequently used in an attempt to achieve a balanced conclusion at excavation sites:
3 levels X 8 examples = 24 drawings used by Ernst Haeckel as supporting evidence for his (evolutionary) Biogenetic Law:
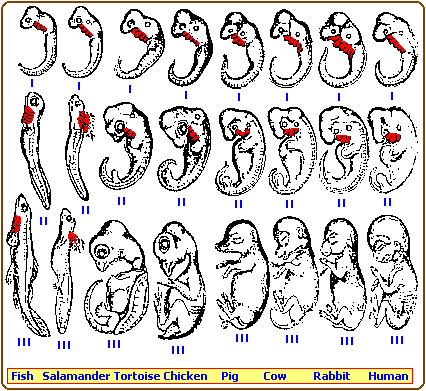
Biogenetic thinking had arisen in the 1820s with the work of anatomist J. Mecker (1781-1833) and zoologist Karl Ernst von Baer (1792-1876), but neither of them developed a theory of evolution. Haeckel's great biogenetic predecessor was the german zoologist Fritz Müller (1821-1897), who formulated the basic laws of biogenesis in 1864. According to Haeckel, "the sequence through which a developing individual passes in its embryological stages (a kind of development we call ontogeny), from the single cell to its fully developed state, is actually a short, compressed replay of the long series of species ancestral to that individual from the earliest geological times to the present." Simply stated, Haeckel's law of biogenesis is that ontogeny (individual development) recapitulates phylogeny (development of the species). He concluded that embryos give us the key to earlier Phylogenetic stages of animal groups.
Chapter 4, page 66, Grzimek's Encyclopedia of Evolution, 1976
The illustration above is a generalized portrayal of the picture used by Ernst Haeckel in his 1866 General Morphologie der Organismen and his more famous 1874 Anthropogenie. The red areas are intended to indicate a similarity of early gill slit formation in the early stages of embryonic development of several different species. However, the illustration used by Haeckel has been called a fraud because it is said to contain false information regarding the actual structures. In other words, Ernst Haeckel is said to have deliberately altered some of the images in order to support his view that ontogeny provides indications of phylogeny, which in simpler terms means that our bodies have a similar developmental design that is exhibited in various body parts during different stages of development. His idea that "Ontogeny recapitulates Phylogeny" is said to be more accurate if it is described as " Embryonic Ontogeny recapitulates Embryogenetic Phylogeny."
Those who argue against the work of Ernest Haeckel as a selected argument against Evolution to support theological views, clearly disregard the simple fact that similarity of structural development does occur and that this does provide clear and unequivocal support for the idea of an ongoing evolutionary process that is not only taking place in biology, but also religion. If their religious doctrine was as absolutely true as they argue vehemently in support of, and their faith in that truth was unswerving and not evolving in response to internal- "midternal"- and external changes, then they would not need to attempt some measure of reconfirmation which takes many forms... Religious ideas also evolve though some prefer to say devolve.
For those of you who are interested in the fraud view:
http://www.answersingenesis.org/docs/1339.asp
Weidenreich considered that Homo sapiens evolved from Gigantopithecus by way of Meganthropus and Pithecanthropus.
3 Mio-Pliocene Hominoidea: Dryopithecus~ Gigantopithecus~ Ramapithecus

3 most common arguments against the Bigfoot-Giganto theory:
http://www.bfro.net/REF/THEORIES/MJM/whatrtha.htm
3 footprint types of Big Foot In the world:
|
Some people can look at pictures of the human brain under different stages of development and see what appears to be a boxing glove shape. |

|
3-jointed penis has been attributed to Bigfoot:
The Triple Jointed Penis is nature's perfect birth control device. Human males have a single penile bone; whereas Bigfoot has a triple-jointed bone that can make a "U" turn, and deposit its sperm outside the female. This handy and efficient form of birth control explains the rarity of Bigfoot today. The triple jointed penis also suggests that Bigfoot was able to engage in athletic mating practices without damaging the bone, and this inspired the creature's scientific name, "Giganticus Erectus Robustus."
Image and information from:
http://www.claytonbailey.com/bigfootskeleton.htm
font color="#ff0000">Three basic types (sizes) of mysterious primate-like creatures with different names from different regions.
| Dwarf or Pygmy (3 to 5 ft. tall) |
Man-sized (5 to 8 ft. tall) |
*Giant (8 to 15 ft. tall) |
| Agogwe - (Tanzania) Alux- (South and Central America) Apamandi - (Zaire) Batutut - (Borneo) Chimanimani - (South Africa) Duende or Tarma - (Peru) Fating'ho - (Senegal) Guayazi - (South America) Higabon - (Japan) Jungli Admi - (India) Kapre - (Philippines) Koolookamba - (Gabon) Maero or Macro - (New Zealand) Mau - (East Africa) Menehune - (Hawaii) Mono Grande or Didi - (Guyana) Nittaewo - (Sri Lanka) Orang-Pendek - (Sumatra) Sehité - (Ivory Coast) Shiru - (Colombia) Teh-lma - (Himalayas) Tokoloshe - (Southern Rhodesia) Ufiti - (Malawi) Vedi - (Croatia) Véle - (Fiji Islands) Xipe - (Nicaragua) |
Aigypan - (Venezuela) Almas - (Caucasus) Arulataq - (Alaska) Barmanou- (Pakistan Afghanistan) Chemosit - (Kenya) Chuchunaa - (Siberia) Ferla Mohr or Brenin Llwyd - (also known as Scotland's Big Grey Man) Gul-Biavan - (Russia, Mongolia) Grendel - (Denmark) Kaptar - (Russia, Mongolia) Khi-Trau - (Laos, Vietnam) Kikomba - (Zaire) Ksy-Giik - (Kazakhstan, Kirghizistan) Mapinguary - (Brazil) Mawas - (Malaysia) Meh-teh - (Himalayas) Muhalu - (West Africa) Nasnas- (Iran) Nguoi Rung - (Vietnam) Sisemite - (Guatemala, Belize) Tano Giant - (West Africa) Ukumarzupai - (Argentina, Chile) Ucumar or Ucu - (Chile Vasitri - (Venezuela) Wa'ab - (Sudan) Windigo - (Quebec) Wudewasa or Tree Eater - (Finland, Croatia) Yowie - (Australia) |
Curinquean - (South America) Dzu-Teh - (Himalayas) Gin-Sung - (China) Kung-Lu - (China) Orang Gadang - (Sumatra) Tok - (China) |
*The third (giant) type is believed by some to be surviving --- Gigantopithecus ---, the largest primate that ever walked the Earth, which, according to established science, went extinct 500,000 years ago.
As is shown in the above list, the creatures are known by many different names, depending on the continent, country, region, and particular area they are supposedly from. All of these (size) types also present some variation as for length and color of hair and some other characteristics, such as feet shape, facial features, limb length, posture, behavior and diet. All of these characteristics further split those (size) types into men-like (Hominids), ape-like (Pongids), bear-like (Ursidaes) and monkey-like (Simioids) creatures. Most of the reports are of creatures described as Hominoids (Hominids and Pongids), with very few Simioids and Ursidaes descriptions.
For additional information, see also:
http://www.occultopedia.com/a/abominable_snowman.htm
Sasquatch
http://www.occultopedia.com/s/sasquatch.htm
Bigfoot
http://www.occultopedia.com/b/bigfoot.htm
Maricoxi
http://www.occultopedia.com/m/maricoxi.htm
Yeti
http://www.occultopedia.com/y/yeti.htm
'X'
http://www.occultopedia.com/x/xcreature.htm
Wildman of China
http://www.occultopedia.com/w/wildman.htm
--- Mysterious Primates ---
http://www.occultopedia.com/m/mysterious_primates.htm
3 large geographical areas (Asia, Australia, North America) for members of the "Bigfoot" family and the hypothetical counterparts. Imagine if you will a similar lineage of development using an Out-of-Africa hypothesis:
For additional information, see also:
http://www.occultopedia.com/a/abominable_snowman.htm
--- Sasquatch ---
http://www.occultopedia.com/s/sasquatch.htm
--- Bigfoot ---
http://www.occultopedia.com/b/bigfoot.htm
--- Maricoxi ---
http://www.occultopedia.com/m/maricoxi.htm
--- Yeti ---
http://www.occultopedia.com/y/yeti.htm
--- 'X' ---
http://www.occultopedia.com/x/xcreature.htm
--- Wildman of China ---
http://www.occultopedia.com/w/wildman.htm
--- Mysterious Primates ---
http://www.occultopedia.com/m/mysterious_primates.htm
3 Historical approaches towards re-constructing a Phylogeny:
...When a disagreement arises, the cladistic approach is to resolve them via "parsimony"... that some may define as an exclusionary "stinginess".)
http://niko.unl.edu/bs101/notes/lecture16.html
3 types of observed shared character states:
http://www.bio.indiana.edu/Courses/S318-Brodie/S318/S318lect24-systematics.html
With respect to the classification of evolutionary
relationships, the following two phylogenetic tree outlines exhibit alternative
approaches: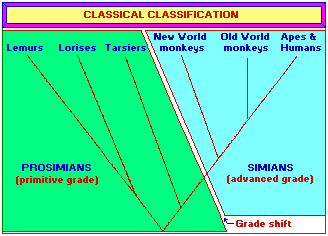
In a classical classification, divisions are based on the grade of organization. Groups that have retained a relatively high proportion of primitive features are allocated to a lower grade, while groups characterized by advanced features are allocated to a higher grade. Members of an advanced grade share specific novel features that define a "grade shift." This classical division scheme, as is portrayed here, separates the six natural primate groups into three groups each. |
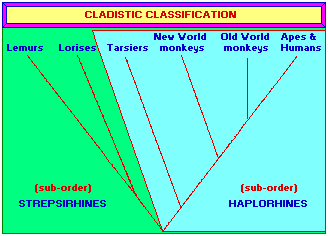
In a cladistic classification, divisions are directly based on the sequence of branching within the tree. Individual groups are therefore clades rather than grades. The initial division in this tree separates lemurs and lorises from tarsiers, monkeys, apes and humans and so the order Primates is subdivided into two suborders Strepsirhini and Haplorhini. One disadvantage to this classification is that very early fossil forms, which are often fragmentary, do not easily separate into one or the other of the two suborders (resulting in the need for a third order?) |
Cladistics can be viewed as bipolar in the sense of describing polarized character states (either a species has a given character or it doesn't - there's no in-between, no overlapping, no combination). This design is similar to the binomial trait of present day computer design (it uses 0's and 1's), which is a mathematical representation of the on/off polarization seen in a common (present day) electrical circuit. However, it may be surmised that if and when computer design advances to the usage of an underlying Trinomial operation consistent with so many three-patterned biological processes, Cladistics will be seen to be very primitive in design... even though some researchers already recognize this on other levels of comparison.) |
3 basic assumptions in cladistics:
http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/clad/clad1.html
For a short view questioning the validity of cladistics:
http://www.utm.edu/~rirwin/391Cladistics.htm
*** Phylogenetic Systematics is a method of classification based on the evolutionary history of organisms, dividing organisms into meaningful groups and subgroups. It was developed by Willi Hennig, an entomologist, in 1950, but was not well accepted until decades later.
Three kinds of similarity amongst phylogenetic relationships:
It is considered as a general rule-of-thumb, that organisms which share many similarities are likely to be closely related; but there are numerous exceptions. Nonetheless, three kinds of similarity can be distinguished:
Definition source:
http://home.about.com/snf.htm?u=http://animals.about.com/library/weekly/aa061901a.htm
3 goals of Systematists:
http://biology.fullerton.edu/biol261/ch/ch10.html
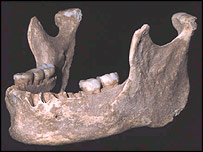
Three different individuals' fossils, from a period in history when modern humans are believed to have shared the continent with Neanderthals, are said to be suggestive of some degree of hybridisation due to interbreeding between modern humans and Neanderthals. This adult male jawbone has been dated to be between 34,000 and 36,000 years old. It has a modern form but has large primitive teeth, according to Professor Erik Trinkaus who is a proponent of the idea of interbreeding having taken place between Neanderthals and modern looking hominids. The fossils were originally discovered in February 2002 in Pestera cu Oase (translated as the "Cave With Bones") by three Romanian cavers in the Carpathian Mountains. The previous oldest modern human remains in Europe are dated to about 30,000 years ago.
For those readers who have an understanding of the threes phenomena, notice
that there are three teeth on the right side and two teeth on the left side.
And for those readers who are not familiar with the idea, the left brain hemisphere/right
body side displays characteristic patterns-of-three and the right brain hemisphere/left
body side displays characteristic patterns-of-two.
Image and information source:
http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/3129654.stm
See the information via the following link concerning the above 2/3 differentiation:
http://www.threesology.org/brain-mind-evolution
Herb O. Buckland
herbobuckland@hotmail.com