page 12
(The Study of Threes)
http://threesology.org
3 types of modern wagon design materials: Steel ~ Wood ~ Plastic
3 types of wheels that can be found on the Radio Flyer Wagons:
- Pneumatic- this wheel consists of an inflatable air tire (or a "Balloon Tire") surrounding a steel wheel.
- Semi-Pneumatic- this wheel has a rubber tire tread. But unlike the pneumatic wheel, these wheels are not inflatable.
- Molded Wheels- This wheel is a durable plastic wheel. Unlike the pneumatic and semi-pneumatic wheels, the molded wheel does not have a steel wheel or a rubber tire.
For more detailed information:
http://www.redwagons.com/noname.html
3 distinct types of portability in Sun Microsystem's Java technology: Source code portability ~ CPU architecture portability ~ OS/GUI portability.
http://www.javaworld.com/javaworld/jw-05-1997/jw-05-portability.html
3 types of tires being recalled due to possible design problems:
- The 15-inch ATX
- The 15-inch ATX II
- The 15-inch Wilderness AT
(New evidence suggests that the practices of both Bridgestone/Firestone and Ford Motor Company were involved in the widespread failure of the tires.)
http://www.wsws.org/articles/2000/aug2000/tire-a26.shtml
3 types of tires were legal in the New York State Ice Racing Association (NYSIRA) and the Adirondack Motorsports Enthusiasts Club (AMEC) in 1997: Studded tires ~ Screwed tires ~ "Specialty, spec" tires.
http://members.aol.com/weissracin/icing.htm
3 Grades for temperature resistance of a tire (branded on the sidewall):
- Grade A = maximum performance level. It withstand a 30-min run at 115 mph.
- Grade B = the tire performs well at 100 mph, but not at 115 mph.
- Grade C = the tire can not withstand a test for a 30 min run at 100 mph.
http://www.safewaytire.com/tirecare.html
3 examples of 3 types of tread pattern:
|
The tread pattern changes across the face of the tire. Usually incorporates larger tread blocks on the outer portion for increased stability during cornering. The smaller inner blocks aid in dissipating water. |
 |
|
Designed to rotate in only one direction, unidirectional tires enhance straight-line acceleration by reducing rolling resistance. They also provide shorter stopping distance. Unidirectional tires must be dedicated to a specific side of the vehicle. Care must be taken when rotating unidirectional tires to ensure that the repositioned tire rotates in the correct direction. |
 |
|
Consistent across the tire's face. Both halves of the treadface are the same design. |
 |
http://www.yokohamatire.com/04a2a.html
3 common types of tire construction:
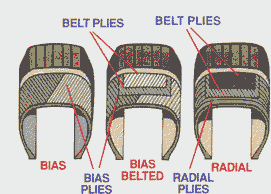
Bias Ply- These tires have two, or more body plies which cross at an angle to the centerline of the tread and which strengthen both the sidewall and the tread area.
Bias Ply Belted- Steel belted variety of the Bias Ply.
Radial Ply- The body cords run across the tire perpendicular to the beads. Radial tires have belt plies which run nearly circumferentially around the tire, under the tread, to stabilize the tread, to strengthen the tread area and add flexibility to the sidewall. By restricting tread movement during contact with the road, the belt plies improve tread life. (Radial tires can also come with steel belts.)
http://4crawler.cruiserpages.com/Diesel/Tires.shtml
3 types of canoes built by the Marshallese people of the Marshall Islands:
- The Walap, which could carry 40 people with supplies for voyages to last more than a month.
- The Tipnol, used to fish in the lagoon.
- The Korkor, fitted with a sail used in the lagoons to fish.
3 types of vegetation on the Marshall Islands: Palm trees ~ Scattered shrubs ~ Grasses.
http://emuseum.mnsu.edu/cultural/oldworld/pacific/marshallese.html
3 types of honey used by the Olympic Cellars winery in their Honey Wine: 80% Clover ~ 10% Blackberry ~ 10% Fireweed.
http://www.olympiccellars.com/honey_wine.htm
3 major types of peanuts are grown in the American South and Southwest:
- Runners: Were introduced in the Seventies and are now the most popular type, are primarily made into peanut butter.
- Virginia peanuts: They are sold roasted in the shell.
- Spanish peanuts: Small round nuts with a reddish-brown skin, Spanish peanuts are used in candies and peanut butter, and are also packed as salted nuts.
3 basic containers in which peanuts are sold: Can ~ Jar ~ Bag.
Information on peanuts was adapted from:
http://www.wholehealthmd.com/refshelf/foods_view/0,1523,110,00.html
3 basic types of brakes used on a roller coaster:
Check Brake- A safety device that allows more than two trains to be on the same circuit, as part of the "block" safety system.
Scarf Brake- Used only to slow down a train, and are usually pre-set.
Trim Brake- A brake used to slow the train running the track.
3 (or 2) train lengths of a flat stretch of track is used as a Brake Run at the station approach, where in-bound trains are halted. Since it is very difficult to stop a train with wet brakes, this area is usually covered to keep the brakes dry during a rainstorm.
A roller coaster car uses 3 different types of wheels:
- Guide Wheel- A set of wheels which guide the train so that it does not leave the track sideways (also known as Side-Friction wheels).
- Road Wheel- A wheel that actually rides on the top of the track.
- Upstop wheel- A set of wheels which ride underneath the track to keep the train from jumping off or leaving the trackwork (also referred to as "Undershot" or "Underside" Friction wheels).
Information was adapted from:
http://www.faqs.org/faqs/roller-coaster-faq/part2/
| 3 Categories of Principal Elements in the Human Body | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| element | symbol | % atoms | % weight | uses |
| organic elements | ||||
| Hydrogen Oxygen Carbon Nitrogen |
H O C N |
62.0 26.0 10.0 1.5 |
9.7 65.0 18.6 3.2 |
water & most molecules water & most molecules all organic molecules protein, nucleic acid |
| major elements | ||||
| Calcium Phosphorus Potassium Sodium Sulfur Chlorine Magnesium |
Ca P K Na S Cl Mg |
.2 .2 .06 .06 .05 .04 .03 |
1.8 1.0 .4 .2 .04 .2 .06 |
bones, teeth, nerve, blood bones, teeth, nucleic acid membrane, nerve, muscle membrane, nerve, muscle protein membrane, water absorption enzyme cofactor, ATP |
| minor (trace) elements | ||||
| Iron Iodine Silicon Flourine Copper Manganese Zinc Selenium Cobalt Molybdenum Chromium Tin Boron Nickel Vanadium |
Fe I Si F Cu Mn Zn Se Co Mo Cr Sn B Ni Va |
.007 .0005 .0000003 [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] |
.0002 [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] [na] |
oxygen transport thyroid hormone membrane calcium migration iron absorbtion, blood regulation bone, tendon, nerve enzymes enzymes, insulin, endocrine vitamin E, detoxication vitamin B12 detoxication enzymes glucose metabolism [unknown] [unknown] enzyme activation cholesterol, fat metabolism |
Above table was adapted from:
http://www.championtrees.org/topsoil/firewater.htm
| Element | ... % | Quantity | Combines mainly with: | Used in the formation of: | |
| Oxygen (organic) |
65 | 98lbs | Calcium, Iron, Sulphur, Phoshorus | Bones, Teeth, Skin, Red Blood corpuscles. | |
| Carbon (organic) |
18 | 27lbs | Silicon, Oxygen | Teeth, Connective Tissue, Skin, Hair, Nails. | |
| Hydrogen (organic) |
10 | 15lbs | Oxygen, Sodium, Chlorine | Blood, and all the Cells in the body. | |
| Nitrogen (organic) |
3 | 4lbs. 8 oz. | Potassium, Chlorine | Muscles, Cartilage, Tissues, Ligaments, Tendons, lean flesh. | |
| Calcium (major) |
2 | 3lbs. | Carbon, Oxygen | Bones and Teeth. | |
| Phosphorus (major) |
1 | 1lbs. 8 oz. | Sodium, Carbon, Oxygen | Blood and Brains. | |
| Potassium (major) |
0.4 | 9.6 oz. | Calcium, Phosphorus, oxygen | Blood, Bones, and all cells. | |
| Sulphur (major) |
.25 | 6 oz. | Potassium, Carbon, Oxygen | Blood | |
| Sodium (major) |
0.25 | 6 oz. | Calcium, Sulphur, Oxygen | Skin, Nerves, Mucous, Membrane | |
| Chlorine (major) |
0.25 | 6 oz. | Nitrogen, Sulphur, Oxygen | Epithelium, Nerves. | |
| Magnesium (major) |
0.05 | 1.2 Oz. | Potassium, Hydrogen, Phosphorus, Oxygen | Blood, Nerves, Muscles. | |
| Fluorine (minor) |
0.2 | 4.8 oz. | Potassium, Sulphur, Oxygen | Nails, Hair, Blood, Skin. | |
| Iron (minor) |
0.008 | 0.2 oz. | Sodium, Hydrogen, Phosphorus, Oxygen | Blood, Bones, Brain, Muscles. | |
| Manganese (minor) |
0.003 | 0.075 oz. | Iron, Oxygen, Hydrogen | Hemoglobin, Lymph, etc. | |
| Silicon (minor) |
0.0002 | Trace | Iron, Phosphorus, Oxygen | Blood, Muscles, Nerves, Skin, Nails, Hair. | |
| Iodine (MINOR) | 0.00004 | Trace | Iron, Magnesium, Phosphorus, Oxygen | Thyroid, Blood, Spine, Nerves, Brain, Bone. |
Above table was adapted from:
http://www.modlife.com/MLG/body.html
3 tables of elemental elements:
The
first list shows elemental composition of the human body by weight, not including the trace elements:
manganese, zinc, copper, aluminum, cobalt, selenium, chromium, etc.:
|
| |
|
Oxygen--- Carbon--- Hydrogen--- Nitrogen--- Calcium--- Phosphorous--- Potassium--- Sulfur--- Sodium--- Chlorine--- Magnesium--- Iron--- Iodine--- |
65% 18% 10% 3% 1.5% 1.0% 0.35% 0.25% 0.15% 0.15% 0.05% 0.0004% 0.00004% |
Using hydrogen as a standard, the above table was converted into elemental composition by mole to reflect stoichiometry:
|
| |
|
Hydrogen--- Oxygen--- Carbon--- Nitrogen--- Calcium--- Phosphorus--- Potassium--- Sulfur--- Sodium--- Chlorine--- Magnesium--- Iron--- Iodine--- |
63% 26% 9% 1.25% 0.25% 0.19% 0.06% 0.06% 0.04% 0.025% 0.013% 0.00004% 0.000002% |
Then it was estimated that the human body is 72% water (an admittedly low estimate) and was removed from the original list, before recalculating the elemental composition by mole, dehydrated:
| By Mole, Dehydrated | |
|
Hydrogen--- Carbon--- Nitrogen--- Oxygen--- Calcium--- Phosphorus--- Potassium--- Sulfur--- Sodium--- Chlorine--- Magnesium--- Iron--- > Iodine--- |
52% 39% 5.6% 1.6% 0.98% 0.77% 0.24% 0.20% 0.15% 0.10% 0.06% 0.0002% 0.000008% |
Above information for these three tables was adapted from:
http://www.madsci.org/posts/archives/jun2000/962225341.Bc.r.html
3 general types of electron transfer in cells: Nucleotides ~ Iron-sulfur ~ Cytrochromes
3 general mechanisms of ion-transport across cell membranes:
- Passive diffusion (or carrier mechanism)
- Pumps (e.g. the Na+-K+ pump)
- Channels (e.g. the acetylcholine receptor channel, the voltage-gated sodium channel)
3 types of antigen presenting cells (APC's) in the immune system: Macrophages ~ Dendritic cells ~ B cells:
http://sprojects.mmi.mcgill.ca/immunology/APC_text.htm
3-patterned mission of the Hamilton Regional Cancer Centre Foundation is to:
- Develop,
- Manage and...
- Distribute charitable resources to...
- Support and enhance patient care,
- Research and...
- Education,
...related to cancer at the Hamilton Regional Cancer Centre and its host hospital.
3 main types of treatment services provided by the Hamilton Regional Cancer Centre:
- Radiation therapy
- Drug treatments (such as chemotherapy)
- Surgery
3 types of research are conducted in the Centre: Basic science in the laboratories ~ Clinical trials ~ Health services research.
Information on the Hamiliton Foundation was adapted from:
http://www.hrccfoundation.on.ca/aboutus.html
3 types of errors can cause the need for revision of surgical hair restoration: Errors of commission ~ Error of omission ~ Nonerrors.
http://www.findarticles.com/cf_0/m0UMR/4_20/54349460/p1/article.jhtml
3 parts categories for automobiles:
- OEM (Orignial Equipment Manufacture)
- OEM After-Market
- Non- OEM After-market
3 common types of air-conditioning systems:
Room,- Room Air-conditioners typically sit in a window and the complete air conditioning system is contained in one box. This system is most suitable for one room only.
Split System,- This system can service more than one room. With the Split System, the compressor (which makes the most noise) is located outside the house and the evaporator is located inside.
Ducted,- is the best solution for air-conditioning a complete house or large areas. It provides maximum flexibility if you want different temperatures in rooms.
Above information on air conditioning systems was adapted from:
http://www.energy.com.au/ea/earetail.nsf/Content/Airconditioning_YourHome
3 points of incentive can be recognized for considering the usage of a tent to provide you with the flexibility to have your wedding Where~ When~ How you want it, providing extra shelter in popular sites such as Gardens~ Public parks~ Historic sites.
3 basic types of sidewalls for tents: Solid white (for privacy)~ Clear vinyl (to let in light)~ The more decorative cathedral-window walls, which also let in some light.
http://www.marthastewart.com/features/features.asp?CID=959&idContentType=5
3 purposes of a well-designed bookcase: Showcase ~ Protect ~ Hide your books... (sometimes all three.)
Books are sometimes used as secret places to conceal valuables such as money, jewels/ jewlery... including watches, money, wills, keys, etc... Books on bookcases are sometimes used to conceal secret passageways (at least in movies).
3 common types of doors on bookcases:
- Standard doors, which open no more than 180 degrees to the sides.
- Top-hinged doors, which open from the bottom to a position at right angles to the bookcase and may be held in place with a locking bracket.
- Pocket or barrister-style doors, which may open to the sides (less commonly) or from the bottom, and then slide into the body of the bookcase.
3 modern-day bookcase composition materials: Solid wood~ Veenered wood~ Metal
3 most common finishes:
Stain- Stain is a material rubbed into the wood to improve grain, figure and color and protect it from moisture, damage and changes in temperature.
Paint- Paints with different properties are applied in layers to form a strong, protective surface.
Specialty finish- Specialty finishes may include various metallic finishes applied to metal pieces or over wood, painted designs such as chinoiserie, and enameling.
Information on bookcases was adapted from:
http://www.furnitureguide.com/buyersguide_bookcases.asp
3 types of asbestos are most commonly used in products:
| Mineral Form: | Chrysotile (90% of asbestos products) |
Amosite | Crocidolite |
| Description: | White, curly | Brown, gray, straight | Blue, straight |
| Chemical Formula: | 3MgO-2SiO2-2H20 | (FeMg)SiO3 | Na2O-Fe2O3-3FeO-8SiO2-H2O |
| Mineral Family: | Serpentine Family | Amphibole Family | Amphibole Family |
The above information on Asbestos was adapted from:
http://www.asbestosnetwork.com/asbestostypes/types.htm
3 main properties of asbestos: Chemical ~ Physical ~ Thermal
http://home.btconnect.com/asbestech/problem.html
3 types of exterior doors: Wood ~ Steel ~ Fiberglass
http://www.moynihanlumber.com/plan/doorwin/door3.htm
3 types of situation comedy:
- Actcom
- Domcom
- Dramedy,
- Action
- Character
- Thought.
each type characterized by differences in their fundamental elements of:
http://www.jcg.jersey.sch.uk/subjects/media/blackadder/sitcomessay2.html
3 common types of cancer:
Basil cell cancer- Usually a bump or nodule resembling a mole that most often appears on the neck, face and hands.
Squamous cell carcinoma- This type of skin cancer shows up in the form of a sore that won't heal.
Malignant melanoma- It often grows from an existing black mole which changes colors, develops a spreading black edge and can spread to other parts of the body. It is the most serious form.
Information on cancer cells was adapted from:
http://www.weeklywire.com/ww/06-29-98/alibi_watch.html
3 to 1 ratio of internet connections as of 04-13-02:
1 of 3- Dial up: Requires a modem. Is the most widely used means of internet connection because of its affordability to the average computer user but it provides the slowest transmission of information. It also ties up the phone line so that no calls can be received nor can a fax machine be used (Though there are computer programs which enable someone to send a fax using their computer.)
2 of 3- DSL (Digital Subscribers Link): DSL technology uses the same connection as your regular phone line, yet allows you to call and surf at the same time. This is possible because the DSL modem allows data transmission over your phone lines at far greater speeds than a traditional modem. You are also provided a dial-up account to use with a traditional modem when you are away from home.
3 of 3- Cable services: use the same coaxial cable connection as your cable T.V. Usually, the cable service provider simply hooks up your PC to a cable modem and you're ready to go. Plus, you can surf the Web and watch your cable programming simultaneously. The cost of DSL and cable are generally about the same.
1 of 1- Satellite: Usually, the service provider installs a satellite dish on or near your home and signals are sent to you just like a satellite T.V. Satellite is generally more costly than DSL and cable and also requires the use of your phone line.
http://www.compaq.com/athome/innovation1/mgced/2_hottopics_broadband.html
As of March 15, 2012, many homes have switched from using the common telephone line to the usage of a cable because of the desire for high speed data transmission and the increased reliance on cell phones. In some cases, an "Air Card" (connected via a cell phone service) is being used by those who want to be connected to the internet "On The Go," which is highly desirable for some business, motor home, camper, and other "auxiliary" mobile lifestyles.
Herb O. Buckland
herbobuckland@hotmail.com