alongside Chirality & Symmetry
page 5
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
Experimental Thinkers as of 3-27-2023
I should also mention that the Scrabble game's scoring methodology often involves single letter, double letter, triple letter; single word, double word, a and triple word variations.
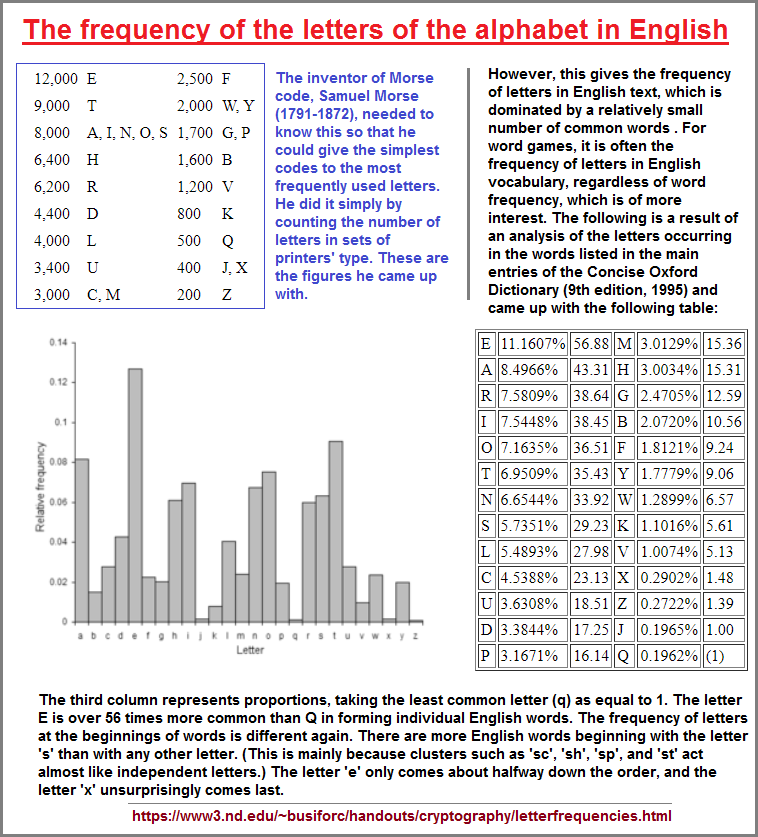
Here is a reference to letter frequencies used in at least one context of the English Language:
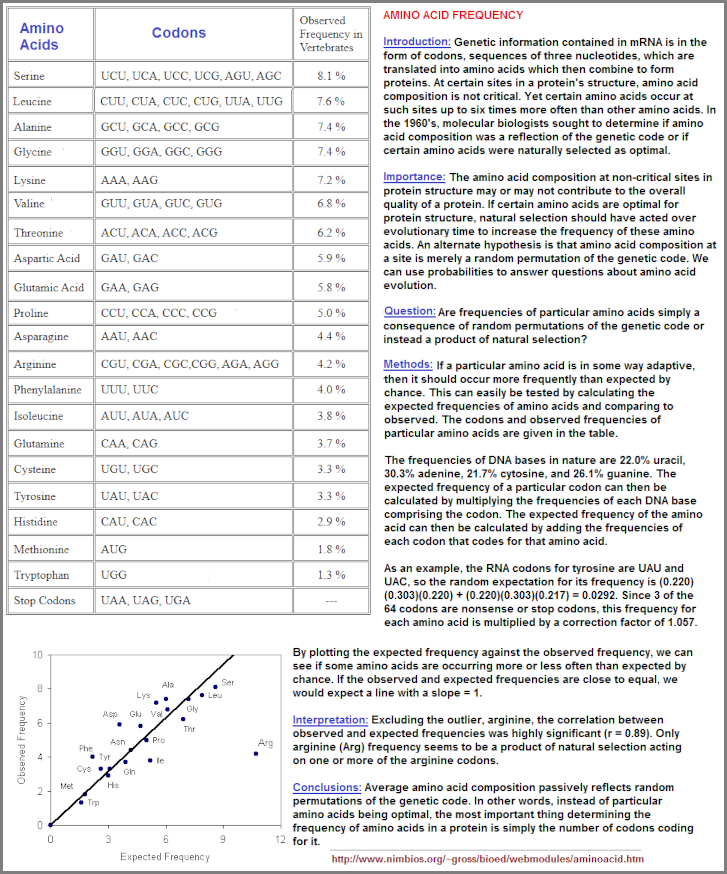
Let us now look at the frequency of amino acids from one report:
Here are two additional references:
The 20 proteinogenic amino acids are present in nature in different amounts, spanning nearly an order of magnitude (UniProt Consortium 2013). The most abundant amino acid in both Swissprot and TrEMBL databases is leucine, whereas tryptophan and cysteine are the least abundant. According to statistical studies, natural protein sequences are indistinguishable from strings of amino acids chosen at random with the abovementioned abundances (Weiss et al. 2000). Amino acid relative abundances are fairly well conserved across organisms, suggesting that a single underlying principle might determine the amino acid composition of proteomes. (Amino Acid Metabolism Conflicts with Protein Diversity by Teresa Krick, Nina Verstraete, Leonardo G. Alonso, David A. Shub, Diego U. Ferreiro, Michael Shub, and Ignacio E. Sánchez.)
Background:
The genetic code is known to be efficient in limiting the effect of mistranslation errors. A misread codon often codes for the same amino acid or one with similar biochemical properties, so the structure and function of the coded protein remain relatively unaltered. Previous studies have attempted to address this question quantitatively, by estimating the fraction of randomly generated codes that do better than the genetic code in respect of overall robustness. We extended these results by investigating the role of amino-acid frequencies in the optimality of the genetic code.
Results:
We found that taking the amino-acid frequency into account decreases the fraction of random codes that beat the natural code. This effect is particularly pronounced when more refined measures of the amino-acid substitution cost are used than hydro-phobicity. To show this, we devised a new cost function by evaluating in silico the change in folding free energy caused by all possible point mutations in a set of protein structures. With this function, which measures protein stability while being unrelated to the code's structure, we estimated that around two random codes in a billion (109) are fitter than the natural code. When alternative codes are restricted to those that interchange bio-synthetically related amino acids, the genetic code appears even more optimal.
Conclusions:
These results lead us to discuss the role of amino-acid frequencies and other parameters in the genetic code's evolution, in an attempt to propose a tentative picture of primitive life. (Optimality of the genetic code with respect to protein stability and amino-acid frequencies by Dimitri Gilis, Serge Massar, Nicolas J Cerf, and Marianne Rooman)
The fact that we have the same 20 amino acids across the spectrum of Nature suggests that maybe this is not random, even if individual amino acid frequencies are. Likewise, the fact that we have approximately 118 chemical elements, regardless of frequency suggests this conservation also is non-random. However, what I am getting at is that while looking at the frequency of singular instances within a group, the group needs to be looked at as well for its frequency. For example, if a team (such as baseball) calls for 9 players (due to a standardized rule in the U.S.) and we intermittently substitute the players with others, the overall quantity is non-random. Another example is a person working odd hours compared to others, and yet still gets in a 40 hour work week just like everyone else.

Here is a short list of other rule-book codes for player quantity:
- Bowling: 1 to Many
- Chess, Martial arts, Boxing: 2
- Wrestling: 2 to several (team match-ups)
- Basketball: 5
- Ice Hockey: 6
- Baseball: 9
- Football, Cricket, Soccer: 11
- Rugby: 13 (union play) or 15 (league play)
Are we inclined to think that the overall count of 20 amino acids is random or randomly specific? And why 20? Is this related to the quantity of fingers and toes and might otherwise suggest we should use a base 20 instead of a base ten in our counting scheme? Are we also to say that the 118 Chemical elements are random, because their proportions can be different on different planets? And yet with respect to amino acids a triplet code is used and in the case of the chemical element chart the elements are arranged in a tripartite fashion of solids, liquids, gases. Ancient and present day peoples have used a variety of schemes in an effort to unravel and illustrate the codes of Nature and its apparent influences. We should note that the themes typically involve a conserved (limited) quantity of categories. In other words, no one typically references an idea with dozens of categorizations:
- Ancient Greek essentials of life: fire- earth- water- air
- Five humors: blood, phlegm, cholera (yellow bile), and melancholy (black bile)
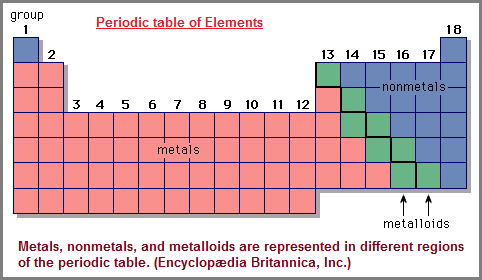
- Periodic table of elements: Metals, Non-metals, Metalloids
- Ancient Native American four types of animals: creeping, flying, four-legged, and two-legged
- 1- 2- 3 naming convention: [Personal name]... [Personal name/Family name]... [Personal name/ Middle name/ Family name]
- U.S. Government sponsored dietary food groupings: fruits, grains, protein, and vegetables
- Ancient religion linked mythology: gods, demi-gods, mortals
- heaven- purgatory- hell
- Wiccan: virgin- mother- crone
- Binomial Nomenclature
- Chinese yin/yang duality
- animal- vegetable- mineral
- slavery/free-man
- Apprentice- Journeyman- Master
- Manager- Assistant Manager- 3rd man
- Computer screen, upper right hand corner: minimize- maximize- close
- Memory: Long term- Short term- Episodic
- Lower class- Middle class- Upper class
- King- Knight- Commoner
- Herbivore- Carnivore- Omnivore
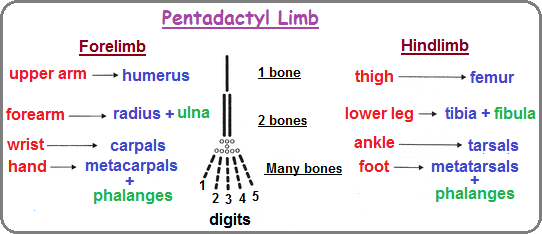
- Pentadactyl limb (comparative anatomy): 1- 2- Many bones
- In Chemistry: 3 exceptions to Octet rule
- Ions or molecules with an odd number of electrons.
- Ions or molecules with less than an octet.
- Ions or molecules with more than eight valence electrons (expanded octet: ex: phosphorus)
- (Exceptions to the Octet rule)
- LGBTQ categorization which places females at the top of the totem hierarchy
- Priestly class- Warrior class- Producer class (Dumezilian tripartite theory)
- 7 stars (Big Dipper/Pleiades) references the number to be associated with Heaven and god
- Monism- Dualism- Triadism- Polyism
- Monotheism- Ditheism- Tritheism- Polytheism
- Trilaminar cell membrane, Bi-lipid layer cell membrane
- Medieval education standard: Trivium (grammar, rhetoric, and logic) and Quadrivium (music, arithmetic, geometry, and astronomy)
- etc...
This review of the Triplet Code's origin involves looking at the triplex of the Sun- Earth- Moon as participators in what one might describe as a collusion... if they were viewed as:
- 3 businesses forced to share the same demographic region because they are permitted to take advantage of deliberately designed (legislatively crafted/fabricated) loop holes put into anti-trust laws of competition. (Otherwise we would have laws to automatically close all unforeseen loopholes.)
- 3 influential religions promoting the product of a single god.
- 3 dominant governments who want the publics of the world involved in a musical chairs game of a politicized chess match.
Whereas we can step back from the trio in a cartoonish animated way to give us a perspective that previous generations would have been amazed, if not overwhelmed at, a more realistic view may not enhance a given reader's appreciation of the dynamics of the three. Here is one example of the triplex as a means to get the reader, so-to-speak, to put a proverbial toe into the forthcoming ocean and waves:

Sun, Earth, Moon animation
Take a look at this next image and see how it resembles the foregoing triplex of planets:

From one subject to the next we see symbolic representations of the same influential external patterns which become embossed and embraced. Differences in physiology, culture, environmental era, nutrition, etc., all play a part on how the impressions are perceived and expressed. If a person is culturally or politically or by gender forced to convey impressions in a given way, they may necessarily do so. The only trouble is that no one is speaking about how the internal impressions and expressed representations are to be changed along the course of incremental deteriorations taking place in the externalities of such pattern influences. In other words, the triplex (Sun, Earth, Moon) are deteriorating.
Mother Earth, Father Sun and the Hand-Maiden Moon all have shelf-life's. Their consequential incrementalities of change are affecting life, resulting in the construction of ideologies meant to serve up rationalizations which provide concurrent acceptance of one's fate along the course towards oblivion. Religion has already adopted the rationalization with the view of an Apocalypse. Multiple others have adopted negative orientations to one or more activities taking place with humanity and even that humanity is a parasite that should be removed so that a better life form might arise. The problem is, the environment into which a so-called better life form would have to arise, is continuing in its direction of death. The Sun, Earth, Moon are both individually and collectively dying. All that has and will be influence by such interactions will develop systems of equilibrium coinciding with this direction of extinction. This includes the Triplet code. The code can be seen in different configurations. Here are a few:
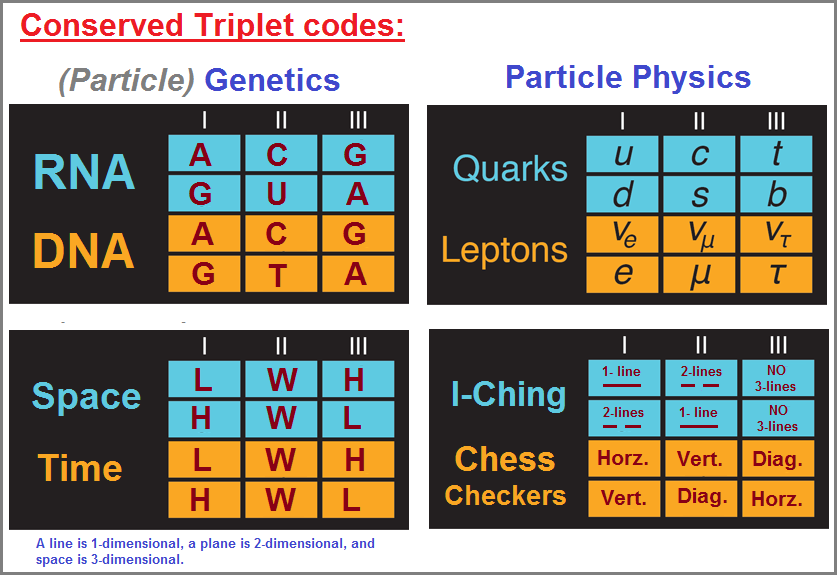
In an effort to avoid an extinction, humanity must direct all its resources to getting off of Earth, then eventually out of the Solar system, and then away from the Galaxy.
In another manner of speaking, all of life was born and continues to be reproduced in several test tubes (3 primordial ponds?) being spun in a centrifuge (whose speed is diminishing), which continues to develop multiple levels of precipitate now being seen as differences in ideological domains of consideration as an extension thereof. I say several ponds because it is not known whether life arose in 1, 2, 3 or Many areas, simultaneously, intermittently, in a successive serialized fashion, etc... Philosophically speaking, three of these (later ideological) domains can be generalized as the previously noted Labels "Business, Politics and Religion", and in some respects might be interpreted to represent growing colonies of fungus... or offshoots as one might diagram a branching tree.
The triplet code arose as an impression of a three-patterned mode of illumination on photo-sensitive micro- and macro-molecules being Chirally spun in an intermittently occurring... reversible geomagnetic field polarity, in which the test tubes had to be offset in a symmetrical alignment so as to keep a balance in the helical motion of the centrifuge. this then suggests that the contents of the test tubes may be periodically mixed, and much later described by variously applied tripartite themes and schemes which seem far removed from a study of biology, that some observers describe as three different races called Orientals, Africans and Occidentals; and still later labeled as Asian, African, European which later became Yellow, Black, White. Such is the case for later psychological and emotional dimensions of basic biological precipitates, which very often express some similitude of pattern design seen occurring with basic biological forms and processes. But such a direction of thought, as a metaphysic, is best kept for another time and place. However, for those interested, let me provide an image directed towards such a discussion:
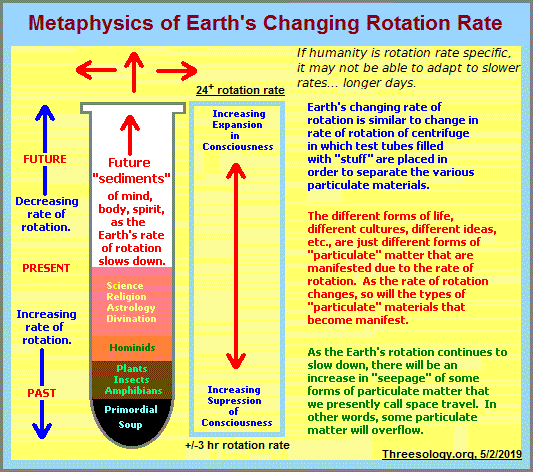
I bring up sociological, cultural and philosophical themes which might appear to some readers as a digression from the main topic, because I see a similarity of patterning between the development of the triplet code and later ideological offshoots as having a psychologically-based Anthropological kinship. The fact that we can see the recurring presence of a triplet code, suggests that whatever may have influenced its pattern may have also played a role in the development of three Germ layers (Endoderm- Mesoderm- Ectoderm), the tripartite brain, and very many three-pattern occurrences in other subject areas. Please note that when discussions involving the developmental loss of the tripartite pattern in some species may seem to some as a contradiction to any notion of some underlying biological predilection for such a pattern to occur and therefore MUST arise, it appears Nature allows for degeneracy but not a developmental plan to exceed the design. In other words it is always in the negative direction of loss or diminishment and not in a positive direction of gain and enhancement. Here is a short reference to the origin and evolution of the Tripartite brain:
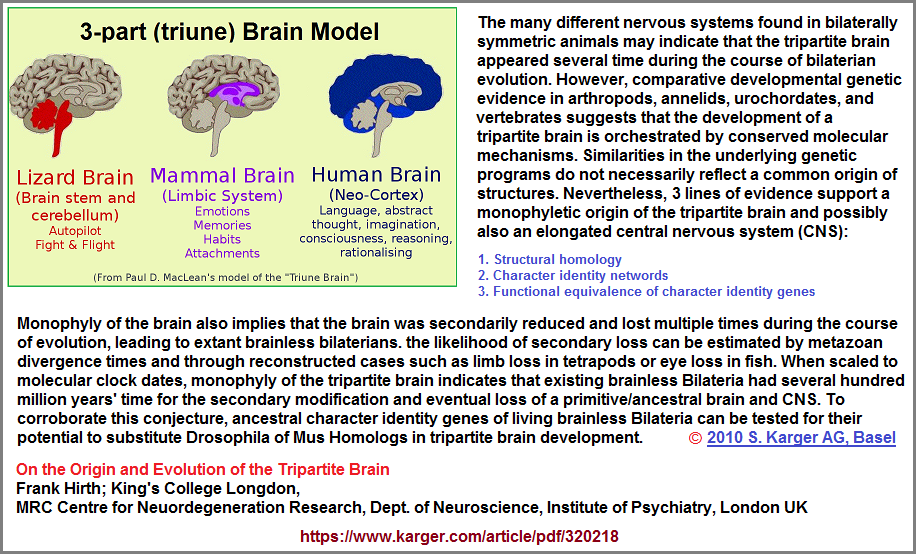
Making note of the same "three" theme (Triplet code → 3 Germ layers → Tripartite brain) may appear to some readers as an excursion into numerology, but if to these we make reference to a recurrence of the same three in physiology, perhaps then you might be persuaded to consider that the influence of the triplet code plays a larger role than one might have previously considered. I other words, in discovering the origin of the code, one might also discover the influential origin of multiple other recurring patterns. And a note about Numerology is in order... that if one takes the time to make a list of the recurring ideological patterns being used by humans in the descriptions of different observations, what we find is a conserved array. I other words, only a handful of numbers are being repeated, just like the repetition of an unrealized code. Let me say the word again: CONSERVED. Just like it is thought the triplet code is an expressed conservation. Out of all the infinity of numbers that humans and Nature have at their disposal, only a very few keep cropping up. One of these is the "3", differentially labeled in accord with the language, the vocabulary of a given subject. Yet, you as a reader want facts. So how about an Anatomical list of "threes" in the human body:
The information on the chart to the right is culled from Dr. McNulty's "Threes in Human Anatomy". For those wanting the chart, I provide this link to the Anatomy_chart.pdf

The physics community has served to dupe the public into thinking that the conservation law is immutable. But I say that which created the conservation may not itself be conserved to the extent it lasts for eternity. Thinking in terms of a human lifetime, or the lifetime of a species, is wholly different when speaking of some larger galactic or Universal position. Conservation laws need not also be taught in such a way as to suggest either universality or freedom from change. Such changes may not necessarily occur in the lifetime of an individual or a species or a solar system or the life of a galaxy, but they may nonetheless be tenably mutable. Let us review the topic of Conservation Law since the Triplet Code is viewed in terms of being Conserved:
Also called law of conservation:
In physics, several principles that state that certain physical properties (i.e., measurable quantities) do not change in the course of time within an isolated physical system. In classical physics, laws of this type govern energy, momentum, angular momentum, mass, and electric charge. In particle physics, other conservation laws apply to properties of subatomic particles that are invariant during interactions. An important function of conservation laws is that they make it possible to predict the macroscopic behaviour of a system without having to consider the microscopic details of the course of a physical process or chemical reaction.
Conservation of energy implies that energy can be neither created nor destroyed, although it can be changed from one form (mechanical, kinetic, chemical, etc.) into another. In an isolated system the sum of all forms of energy therefore remains constant. For example, a falling body has a constant amount of energy, but the form of the energy changes from potential to kinetic. According to the theory of relativity, energy and mass are equivalent. Thus, the rest mass of a body may be considered a form of potential energy, part of which can be converted into other forms of energy.
Conservation of linear momentum expresses the fact that a body or system of bodies in motion retains its total momentum, the product of mass and vector velocity, unless an external force is applied to it. In an isolated system (such as the universe), there are no external forces, so momentum is always conserved. Because momentum is conserved, its components in any direction will also be conserved. Application of the law of conservation of momentum is important in the solution of collision problems. The operation of rockets exemplifies the conservation of momentum: the increased forward momentum of the rocket is equal but opposite in sign to the momentum of the ejected exhaust gases.
Conservation of angular momentum of rotating bodies is analogous to the conservation of linear momentum. Angular momentum is a vector quantity whose conservation expresses the law that a body or system that is rotating continues to rotate at the same rate unless a twisting force, called a torque, is applied to it. The angular momentum of each bit of matter consists of the product of its mass, its distance from the axis of rotation, and the component of its velocity perpendicular to the line from the axis.
Conservation of mass implies that matter can be neither created nor destroyed—i.e., processes that change the physical or chemical properties of substances within an isolated system (such as conversion of a liquid to a gas) leave the total mass unchanged. Strictly speaking, mass is not a conserved quantity. However, except in nuclear reactions, the conversion of rest mass into other forms of mass-energy is so small that, to a high degree of precision, rest mass may be thought of as conserved.
Conservation of charge states that the total amount of electric charge in a system does not change with time. At a subatomic level, charged particles can be created, but always in pairs with equal positive and negative charge so that the total amount of charge always remains constant.
In particle physics, other conservation laws apply to certain properties of nuclear particles, such as baryon number, lepton number, and strangeness. Such laws apply in addition to those of mass, energy, and momentum encountered in everyday life and may be thought of as analogous to the conservation of electric charge. (See also symmetry.)
The laws of conservation of energy, momentum, and angular momentum are all derived from classical mechanics. Nevertheless, all remain true in quantum mechanics and relativistic mechanics, which have replaced classical mechanics as the most fundamental of all laws. In the deepest sense, the three conservation laws express the facts, respectively, that physics does not change with passing time, with displacement in space, or with rotation in space. ("conservation law." Encyclopædia Britannica, 2013.)
Now let us look at symmetry as used in physics, all the while imagining that one is reading an article about basic biological configurations:
Symmetry: in physics, the concept that the properties of particles such as atoms and molecules remain unchanged after being subjected to a variety of symmetry transformations or “operations.” Since the earliest days of natural philosophy (Pythagoras in the 6th century BC), symmetry has furnished insight into the laws of physics and the nature of the cosmos. The two outstanding theoretical achievements of the 20th century, relativity and quantum mechanics, involve notions of symmetry in a fundamental way.
The application of symmetry to physics leads to the important conclusion that certain physical laws, particularly conservation laws, governing the behaviour of objects and particles are not affected when their geometric coordinates—including time, when it is considered as a fourth dimension—are transformed by means of symmetry operations. The physical laws thus remain valid at all places and times in the universe. In particle physics, considerations of symmetry can be used to derive conservation laws and to determine which particle interactions can take place and which cannot (the latter are said to be forbidden). Symmetry also has applications in many other areas of physics and chemistry—for example, in relativity and quantum theory, crystallography, and spectroscopy. Crystals and molecules may indeed be described in terms of the number and type of symmetry operations that can be performed on them. The quantitative discussion of symmetry is called group theory.
Valid symmetry operations are those that can be performed without changing the appearance of an object. The number and type of such operations depend on the geometry of the object to which the operations are applied. The meaning and variety of symmetry operations may be illustrated by considering a square lying on a table. For the square, valid operations are:
(1) rotation about its centre through 90°, 180°, 270°, or 360°. (2) reflection through mirror planes perpendicular to the table and running either through any two opposite corners of the square or through the midpoints of any two opposing sides. (3) reflection through a mirror plane in the plane of the table.There are therefore nine symmetry operations that yield a result indistinguishable from the original square. A circle would be said to have higher symmetry because, for example, it could be rotated through an infinite number of angles (not just multiples of 90°) to give an identical circle.
Subatomic particles have various properties and are affected by certain forces that exhibit symmetry. An important property that gives rise to a conservation law is parity. In quantum mechanics all elementary particles and atoms may be described in terms of a wave equation. If this wave equation remains identical after simultaneous reflection of all spatial coordinates of the particle through the origin of the coordinate system, then it is said to have even parity. If such simultaneous reflection results in a wave equation that differs from the original wave equation only in sign, then the particle is said to have odd parity. The overall parity of a collection of particles, such as a molecule, is found to be unchanged with time during physical processes and reactions; this fact is expressed as the law of conservation of parity. At the subatomic level, however, parity is not conserved in reactions that are due to the weak force.
Elementary particles are also said to have internal symmetry; these symmetries are useful in classifying particles and in leading to selection rules. Such an internal symmetry is baryon number, which is a property of a class of particles called hadrons. Hadrons with a baryon number of zero are called mesons, those with a number of +1 are baryons. By symmetry there must exist another class of particles with a baryon number of -1; these are the antimatter counterparts of baryons called antibaryons. Baryon number is conserved during nuclear interactions. ("symmetry." Encyclopædia Britannica, 2013.)
Date of Origination: Monday, 6th March 2023... 4:54 AM
Initial Posting: Monday, 27th March 2023... 11:11 AM